Mitsubishi Outlander: Basic Brake
General Information
Brake systems with higher reliability and durability have achieved distinguished braking performance.
FEATURES
IMPROVEMENT OF BRAKING PERFORMANCE
- In addition to the 10-inch single brake booster, the small and long stroke-type master cylinder is used to achieve the downsizing and secure the assist force.
- The installation of 16-inch ventilated disc brake on the front axle and 16-inch solid disc brake on the rear axle achieves the secure braking force and direct braking feeling.
IMPROVEMENT IN SAFETY
- The 4-wheel anti-lock brake system (4ABS) has been installed to prevent slippage resulting from the wheel lock and assure stable vehicle posture and driveability.
- Electronic control braking force distribution system (EBD) has been adopted to assure the maximum braking force independently of the passenger' position in the vehicle.
- X-type piping of brake lines have been adopted for the front and rear wheels.
- Audible wear indicator has been adopted to the front and rear brake pads to warn the driver of the wear limit.
- The 10-inch single brake booster with brake assist mechanism, which determines an emergency exists based on the brake pedal depression speed and force and provides the maximum braking force, has been adopted.
SERVICE QUALITY IMPROVEMENTS
- Diagnostic function has been adopted to ABS for easier inspection.
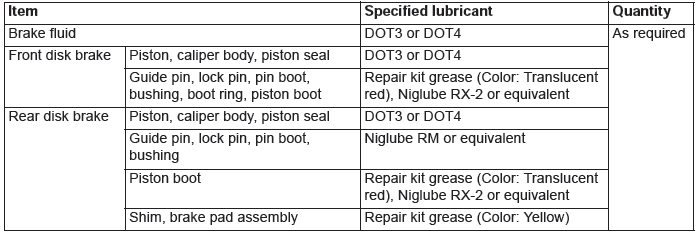
- Brake fluid reservoir, master cylinder, and brake booster have been integrated for downsizing and better serviceability.
BRAKE ASSIST MECHANISM
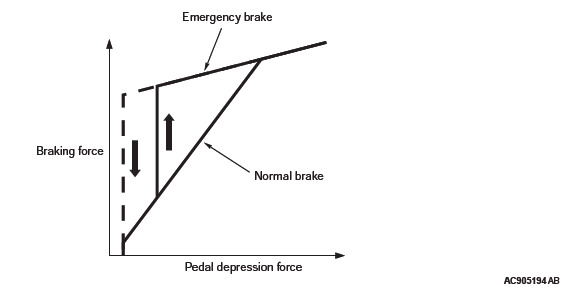
When the driver suddenly applies the brake, generally there is a tendency that a driver depresses the brake pedal quickly but not strong enough, or depresses the pedal once but reduces the depression force immediately after that. In this case, a sufficient braking force cannot be obtained, resulting in a longer stopping distance.
This brake booster with brake assist mechanism recognizes the status as emergency when the driver depresses the brake pedal quickly; it increases the assist force to the maximum value and maintains the output value of the brake booster to activate ABS.
Even if the driver reduces the depression force immediately after depressing the brake pedal quickly, this brake booster maintains the status where the maximum assist force is being applied until no depression force is applied to the brake pedal.
General Specifications
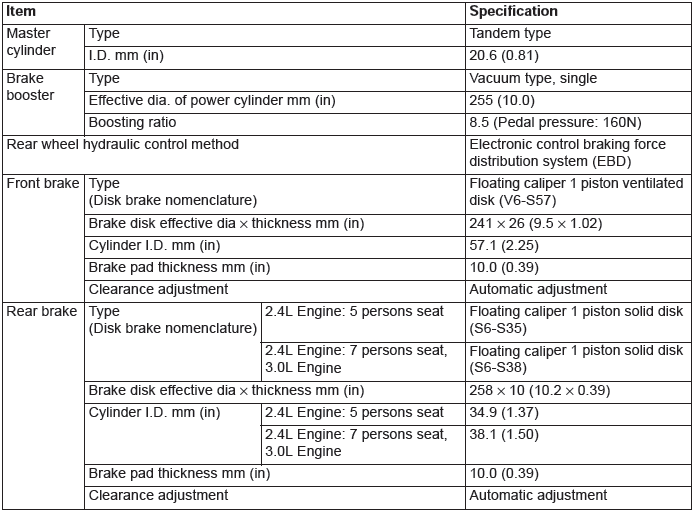
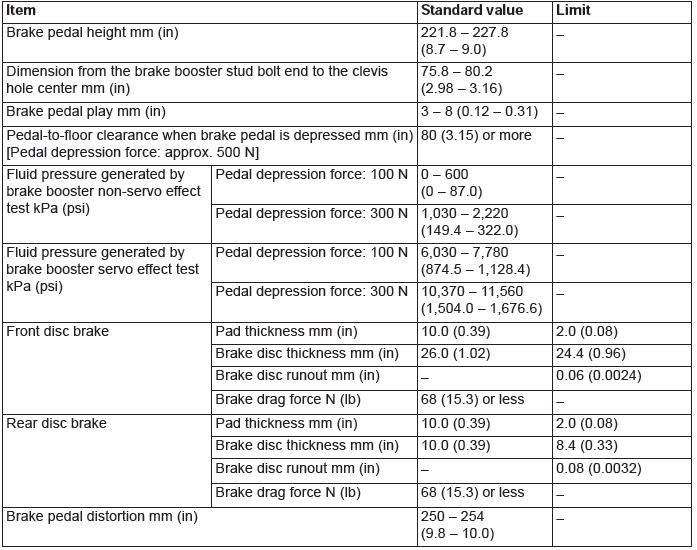
Service Specifications
Lubricants